1. Scan and restore corrupted system files using "System File Checker" utility
Before running this utility, make sure to run Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) tool by running this command in elevated cmd window: DISM.exe /Online /Cleanup-image /Restorehealth
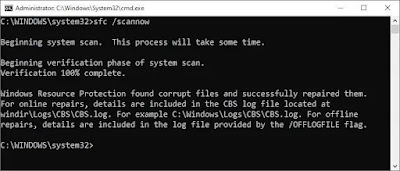
DISM uses Windows Update to provide the files that are required to fix corruptions. But if the OS is already broken and most of the components are not working in Windows, this command would not be so helpful.After running the DISM command, in the same elevated command prompt window, run the following command sfc /scannow and press enter key. This command will scan all protected system files, and replace corrupted files with a cached copy that is located in a compressed folder at C:\Windows\System32\dllcache.
2. Set the process priority to low, if it is utilizing too much CPU resource
Open task manager and check which process is using more CPU. Right click on the process and click on "Go to details" and then it would show up the actual exe file which is creating that process. Simply right click on the exe file name, then click on "Set Priority" and click "Low". This step would ensure that the process would be restricted from using maximum CPU resources.
3. Install all pending Windows updates
Click on Start and then click on Settings. From there, open Windows updates and check for all the available updates (cumulative, feature updates and other optional updates) and install them. Once the updates are installed, restart the system and check for the CPU utilization.
4. Install all system drivers (including BIOS and Intel Turbo Boost Driver)
Open your system manufacturer's website and check for the downloads section. From the downloads section, download all the latest drivers for your system. Drivers include BIOS, VGA, Audio, Chipset, Dynamic Tuning Driver, Intel Turbo Boost driver etc. If your manufacturer provides any tool for auto update of drivers (such as HP Support Assistant, Dell Support Assistant, Lenovo Vantage etc), then use the tool to auto update the drivers to the latest version.
But I would personally recommend using IObit Driver Booster tool which checks for the best performing drivers for your device and auto downloads and installs them. I am personally using it and trust me, it is awesome.
Once the drivers are updated, restart the system and check the system performance. Make sure not to miss updating the BIOS to the latest version, because BIOS would usually require manual updation from manufacturer's website.
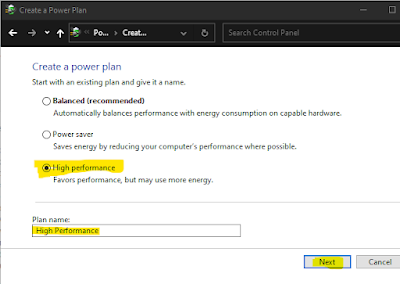
5. Create a high performance power plan
Most of the times, due to balanced power plan of the OS, processor is not utilized properly by the system processes which cause malfunction with the processor and system processes. This causes incorrect CPU utilization. So it is recommended to create a high performance power plan and set it as default so that system could run with its maximum potential. To create a high performance power plan, follow the steps below:
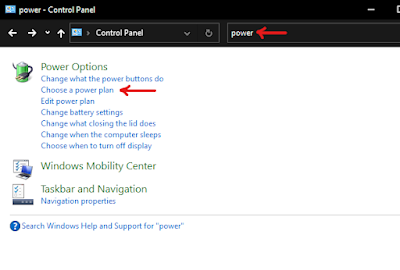
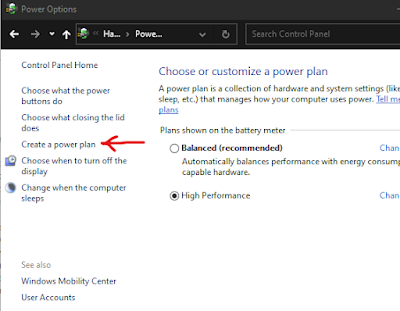
> Open control panel and in the search bar, type power, and then click on "Choose a power plan" and set the power plan to "High Performance". If it is not available in your system, then click on "Create a Power Plan". Now select "High Performance" and type the name of your power plan (you may use any name, I used High Performance) and then click on Next and finish. Once you are done with creating the power plan, use it in power options. It should bring back the CPU utilization to normal.
6. Modify settings in registry
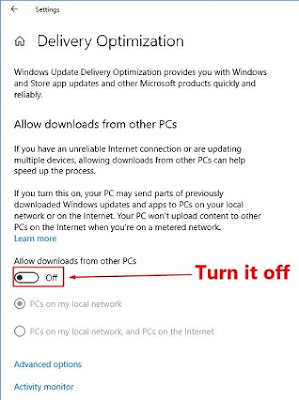
7. Disable P2P Share for Windows Updates
8. Uninstall Sophos client or update it to the latest version
9. Perform clean boot and run a complete virus scan using Malwarebytes anti malware utility
10. Factory Reset the OS/Reinstall Windows
11. Contact system manufacturer for hardware tests and part replacement
Additionally, you can use tuneup utilities such as IObit Advanced System Care utility or any other good tuneup utility to optimize your system performance.











My issue was fixed. Thanks
ReplyDeleteGreat Article
ReplyDelete